Mastering Cost Risk with the CRED Model: A New Approach to Managing Uncertainty

For project managers across industries—whether in software development, manufacturing, or engineering design—estimating project scope in terms of cost, effort, schedule, and risk is a common challenge.
Before a project begins, your company needs to decide if it’s feasible within the budget. You may also need a ROM estimate when submitting proposals to secure new business.
Table of Contents
What is a ROM Estimate and Why Do I Need One?
A Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) estimate is a preliminary estimate which provides a high-level, “ballpark” figure for a project. This initial estimate helps assess if a project will cost $50,000 or $5,000,000, or whether it will take six weeks, six months, or six years.
ROM is crucial in project management and planning phase as it provides a rough cost estimate, offering a valuable budget estimate that helps determine the feasibility and scope of a project in its very early stages.
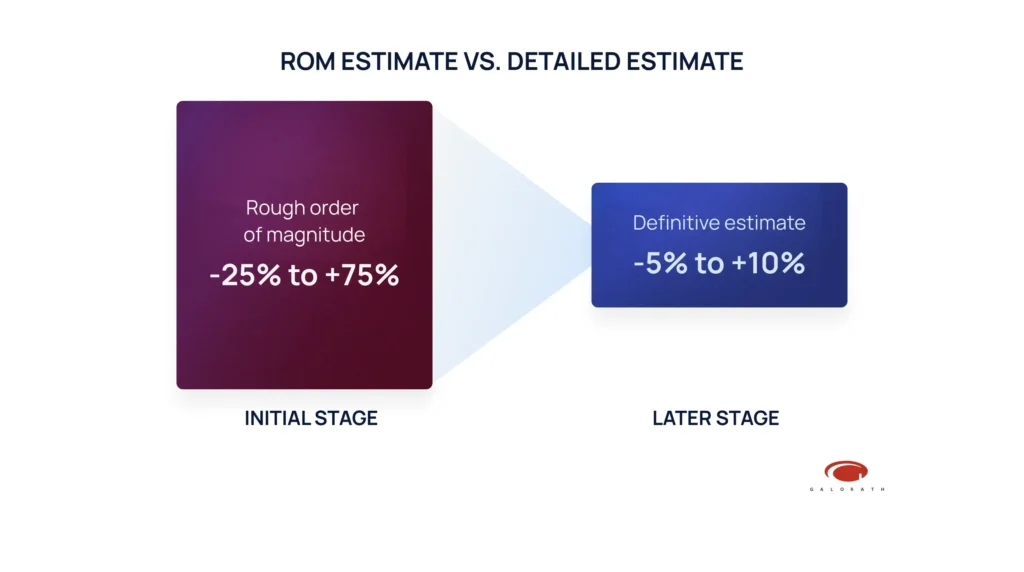
According to the PMBOK® Guide, a ROM estimate can vary between -25% and +75% of the final cost, with business case analysis often ranging from -50% to +50% for technology projects. A ROM estimate can help determine feasibility and whether to pursue a project proposal.
However, once a ROM is developed, a detailed estimate will provide better clarity regarding project costs, schedule, and resource allocation. Since ROM estimation occurs early in the project lifecycle, it plays a key role in the planning phase – helping stakeholders assess feasibility and set expectations before detailed cost and resource planning begins.
How to create Rough order of magnitude?
There are various methods to develop a ROM estimate based on the project type and the estimation techniques employed, with parametric and analogous estimation often being the favored approaches.
A good starting point involves considering multiple factors, leveraging historical data and your past project experience to make an informed guesstimate. To prevent bias, rely on thorough research and actual data to guide your estimation.
Viewing the cost landscape through a range offers a broad perspective for the project’s estimated cost. Although some detailed information might be missing, it’s a solid starting point for moving forward with your project plan.
SEER Tools for ROM estimate
SEER offers a suite of interoperable products that capture all known project details and simulate potential unknowns, giving you a range of probable outcomes and a most likely estimate. No matter the project type—whether it’s developing a mobile app, designing an avionics system, or planning a manufacturing process—SEER solutions provide clarity.
- SEER for Software: Estimates cost, schedule, effort, defects, and risk for software development and maintenance projects.
- SEER for Information Technology: Offers total cost of ownership for IT projects, covering infrastructure, services, operations, and support.
- SEER for Hardware: Covers total cost of ownership for hardware and electronics development, from concept through production and retirement.
- SEER for Manufacturing: Estimates detailed manufacturing and assembly costs for a wide range of processes, identifying cost drivers and production risks.
SEER’s models are parametric-based with an extensive knowledge base, allowing the use of built-in intelligence to derive initial parameter settings based on industry standards—even when project parameters are not fully defined.
ROM vs Detailed Estimate
Preliminary estimates and detailed estimates serve distinct purposes in the project estimation process, each with its own level of accuracy and application timing.
A preliminary estimate is often generated during the project’s early stages, while a detailed estimate is developed once more specific project information becomes available, usually during the planning phase. This estimate is characterized by a higher degree of accuracy, and according to PMBOK® often within -5% to +10%, as it incorporates detailed project specifications, resource allocation, and scheduling.
Detailed estimates require a bottom up estimating approach, where each component of the project is meticulously analyzed and costed, resulting in a precise estimate that guides the project’s budget and execution. This comprehensive approach ensures that project managers have a reliable foundation for managing project costs and resources effectively as the project moves forward.
Moving from ROM to Detailed Estimate—An Example
Imagine you’re developing a sales toolkit using SEER for Software. Initially, you may only know the basics:
- A client database
- A central repository
- A product demonstration package
With additional information—like a contact manager for the database, replication capability for the repository, and multimedia tools for the demo package—you can expand the work breakdown structure for a more precise estimate.
Using SEER for Software, you can assign unique parameter settings, development methods, quality standards, and staff profiles to each component, enhancing the estimate’s accuracy and credibility. SEER also supports trade-off analyses, allowing alternative solutions within the work breakdown structure.
Built-In Risk and Uncertainty Analysis
SEER tools use probabilistic models with built-in risk and uncertainty analysis. When estimating, input values can be classified as:
- Least
- Likely
- Most
For instance, if the project’s programmer experience level is uncertain, you could specify a minimum experience level for the worst-case scenario, a mixed experience level for the likely scenario, and an experienced team for the best case. SEER then returns a probability estimate, showing the likelihood of achieving project goals.
This analysis allows for what-if scenarios, like changing team composition, outsourcing certain tasks, or adjusting scope, so you can achieve confidence that the project will meet budget and schedule targets.
Integration with Microsoft Project or P6
Once a ROM or detailed estimate is generated in SEER, it can be transformed into a detailed, task-oriented project plan in Microsoft Project or P6. This lets you:
- Use custom life cycle templates with best practices for your project plans
- Customize labor categories to match your organization’s staffing approach
Summary
Project managers need reliable, repeatable tools to develop ROM estimates effectively. SEER provides a robust solution for creating these estimates, offering tools that integrate parametric and probabilistic analysis. SEER also simplifies the transition from a high-level ROM estimate to a detailed estimate and project plan, supporting you from project inception through completion.
Contact Us
Discover how SEER tools can help your organization eliminate guesswork from estimating, planning, and project control.
10 Step Estimation Process Sample Checklist
View our 10 Step Estimating Process Checklist. This checklist should be tuned to the individual company’s needs and suggestions.
Estimating Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Find out how you can use Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) model to create an estimate which includes all the costs generated over the useful life of a given application.
Should Cost Analysis
Learn how Should-Cost Analysis can identify savings opportunities and drive cost efficiency in procurement and manufacturing processes.
ROM Estimate: The First Step Towards a Detailed Project Plan
Find out what ROM (rough order of magnitude) estimate is and why is it a crucial element of every project planning cycle.
Software Maintenance Cost
Find out why accurate estimation of software maintenance costs is critical to proper project management, and how it can make up to roughly 75% of the TCO.