Mastering Cost Risk with the CRED Model: A New Approach to Managing Uncertainty
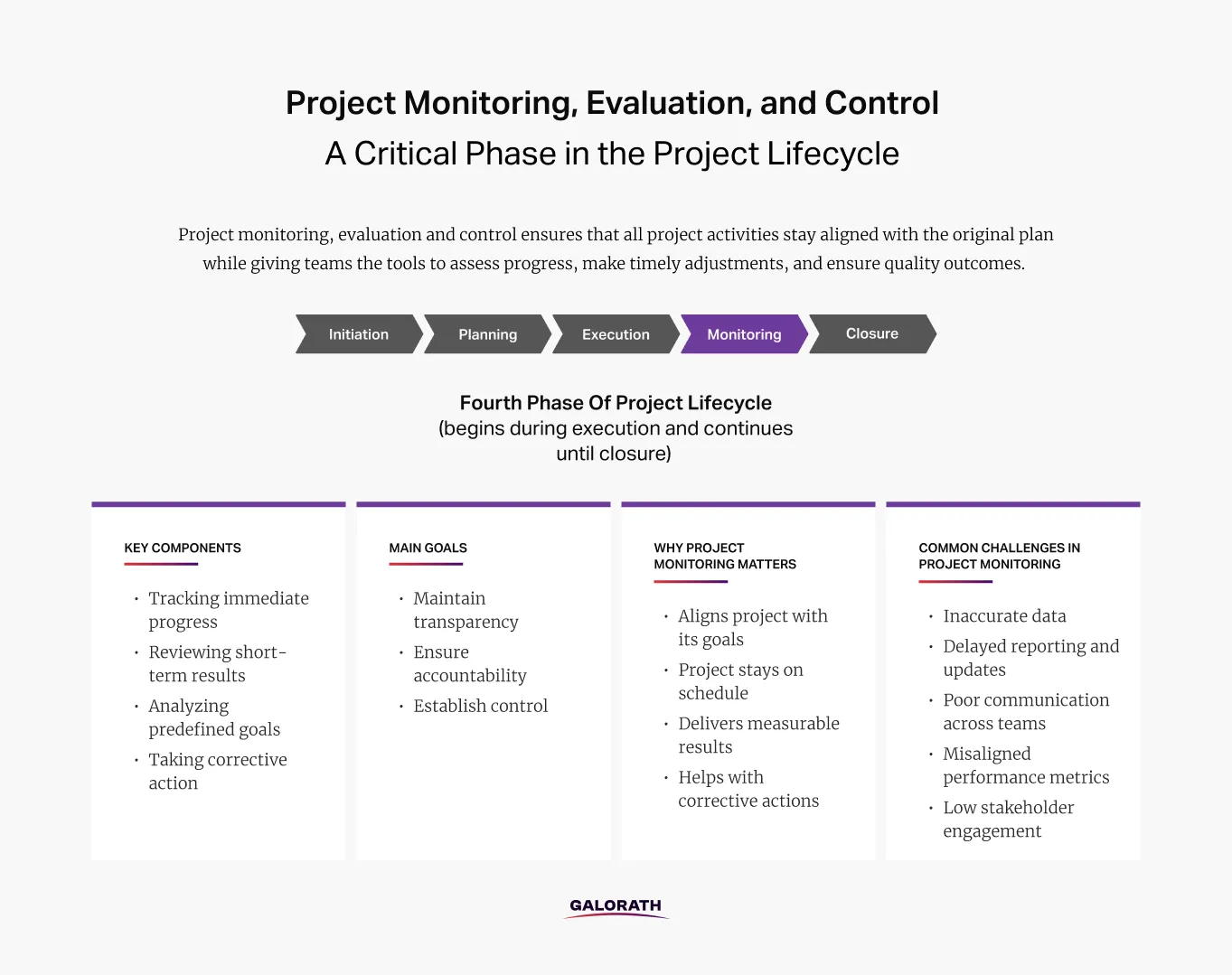
Project monitoring, evaluation, and control is a formal phase of the project lifecycle that begins during execution and continues through closure. It helps keep project activities aligned with the original plan while giving teams the ability to assess progress, adjust quickly, and deliver high-quality outcomes.
Project status serves as a core metric during this phase, guiding decisions, identifying performance gaps, and helping teams stay on schedule and within scope.
This phase deals with the tactical management of an active project. Unlike project performance management, which focuses on strategic alignment and long-term efficiency across an organization, monitoring and control concentrate on real-time execution and immediate results.
Monitoring involves tracking ongoing work and comparing it against the project baseline. Evaluation looks at short-term outcomes to determine whether goals are being met. Control uses this information to take corrective action and steer the project back on course when needed. Together, these functions form a continuous feedback loop that supports better delivery and informed decision-making.
This image provides an overview of project monitoring, covering what it is, its key components and goals, why it’s essential for successful delivery, and the common challenges teams face during this phase.
What is project monitoring?
Project monitoring is the process of systematically tracking, reviewing, and analyzing a project’s progress to ensure that it aligns with the predefined goals, scope, timeline, and budget. Monitoring helps project managers and stakeholders understand how well the project is performing, identify potential risks or delays, and make informed decisions to keep everything on track.
This involves tracking metrics such as task completion rates, budget usage, resource allocation, and milestone achievements. Tools like dashboards, Gantt charts, and performance reports are commonly used during monitoring to visualize progress in real time.
The goal of project monitoring is to maintain transparency, accountability, and control throughout the execution phase of a project. It allows project managers to detect deviations early, assess performance, and implement corrective actions before problems escalate.
Project monitoring is typically continuous and occurs in parallel with execution. This ensures that data is collected in real time and used to support decision-making. It is different from project evaluation, which is more reflective and often conducted after project milestones or completion. Monitoring focuses on “what is happening now” rather than “what happened.”
What is project evaluation?
Project evaluation is the process of assessing a project’s outcomes, impact, and overall performance after specific milestones or upon completion. Evaluation helps determine whether a project has met its objectives, delivered value, and achieved the desired results for stakeholders.
Unlike project monitoring, which occurs continuously during execution, project evaluation is conducted at defined points-typically at the end of a phase, a milestone, or the entire project.
There are two main types of project evaluation: formative and summative. Formative evaluation is conducted during the project to provide feedback and guide improvements. Summative evaluation takes place at the end and focuses on outcomes and long-term impact. Both approaches provide valuable insights for improving future projects and refining processes.
Project evaluation involves reviewing documentation, collecting data from performance metrics, and obtaining feedback from stakeholders. Teams often evaluate factors such as scope compliance, budget adherence, schedule performance, risk management effectiveness, and stakeholder satisfaction. These insights are compiled in a post-project report or lessons-learned document that supports organizational learning.
One of the main goals of project evaluation is accountability. Evaluation holds teams responsible for delivering results and provides proof of return on investment. It also supports transparency by offering stakeholders a clear view of how resources were used and whether strategic goals were met.
Project evaluation is essential for continuous improvement. The findings can highlight strengths in planning and execution while identifying areas where methods, tools, or decisions could be enhanced.
What is project control?
Project control is the process of tracking, analyzing, and influencing project performance to ensure alignment with the original plan. This phase involves making data-informed decisions and taking corrective actions to keep the project on scope, on schedule, and within budget.
Project control is more than just oversight and it involves taking proactive steps to improve outcomes. It plays a critical role in translating performance data into real-world decisions that affect the project’s success.
Project control relies heavily on measurable indicators such as earned value, cost performance index (CPI), schedule performance index (SPI), and other key performance indicators (KPIs). These metrics help project managers identify where performance is lagging and determine the cause. When actual results deviate from the project baseline, control strategies are triggered to restore alignment. The project baseline — which includes the approved scope, schedule, and cost baselines — serves as the reference point for these comparisons, ensuring that performance is measured against a formally agreed plan.
Unlike project evaluation, which occurs at the end of a phase or project, project control is continuous and responsive. It starts during execution and continues until closure, making it essential for real-time issue resolution and agile adaptation. Without effective control mechanisms, minor issues can evolve into major problems that delay delivery and increase costs.
Project control also involves managing stakeholder expectations. When priorities shift or deliverables change, the control process helps ensure that all parties remain informed and aligned. This minimizes miscommunication, reduces resistance to change, and maintains trust.
Ultimately, project control is what turns insights into action. It bridges the gap between planning and execution by enabling dynamic decision-making, fostering accountability, and supporting successful outcomes.
The following graph compares project monitoring, evaluation, and control—clarifying their distinct roles, timing, and contributions to effective project oversight and decision-making.

Project Monitoring vs. Project Control
Project monitoring tracks progress and performance against the plan, using data and KPIs while project control uses that data to take corrective actions, adjusting scope, schedule, or resources to keep the project on track.
Together, monitoring and control form a feedback loop. Monitoring provides the diagnostic insights, and control delivers the prescribed response. A project with strong monitoring but no control can identify problems but fail to act. Conversely, a project that attempts control without monitoring lacks the data to guide effective decisions.
Importance of project monitoring, evaluation, and control
The importance of project monitoring, evaluation, and control lies in their combined ability to ensure that a project stays aligned with its goals, stays on schedule, and delivers measurable results. These three functions work together to provide visibility, accountability, and continuous improvement throughout the project lifecycle.
Together, these three pillars of project management provide a structured approach to managing complexity. This integrated approach not only helps meet deadlines and budgets but also improves communication, strengthens stakeholder confidence, and ensures quality outcomes.
Other benefits include improved risk management, clearer visibility into performance, better alignment with organizational goals, and the ability to document successes and failures for future use.
By applying a consistent approach to project monitoring, evaluation, and control, organizations support continuous improvement. This loop helps ensure that projects do not simply reach completion, but also deliver lasting value. Whether managing a construction effort, launching a digital product, or executing a strategic initiative, these practices are essential for success.
Key Components to Monitor in a Project and How to Track Them Effectively
There are several critical components that project managers should focus on during the monitoring phase. Each one provides insight into different aspects of the project and helps stakeholders make informed decisions to ensure success. Below is a comprehensive list of these components and the best ways to track them effectively.
1. Project Scope
Project scope must be monitored to ensure that all work stays within the approved boundaries and that no unplanned tasks are added without proper change control. Managing scope helps prevent scope creep, which can derail timelines and increase costs.
To track scope, use a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to break down deliverables into manageable tasks. Implement a change management process to evaluate any proposed scope changes and assess their impact. Regularly reviewing scope with stakeholders helps keep the project aligned with original goals.
2. Timeline and Milestones
Timeline and milestones need to be monitored to verify that the project is progressing according to schedule. Falling behind schedule can lead to missed deadlines and reduced stakeholder satisfaction.
Use Gantt charts or project scheduling tools like Microsoft Project or monday.com to visualize timelines and task dependencies. Hold regular progress meetings and milestone reviews to assess the status of deliverables and adjust schedules as needed.
3. Budget and Costs
Budget and costs must be tracked to ensure that the project remains within financial limits. Monitoring expenditures helps identify overspending early and allows for corrective action.
Leverage budgeting tools and financial tracking software to compare actual versus planned spending. Generate cost performance reports and maintain regular budget reviews to identify trends and anomalies. Tools like Earned Value Management (EVM) are useful for assessing cost efficiency.
4. Resources and Workload
Resources and workload should be monitored to ensure that the team is operating efficiently without being overburdened. Proper resource management improves productivity and prevents burnout.
Use capacity planning tools and workload dashboards to view each team member’s assignments. Reallocate tasks as necessary to balance workloads. Track availability and utilization rates to make informed staffing decisions.
5. Risk and Issues
Risk and issues require continuous monitoring to prevent them from escalating into major problems. Identifying risks early and managing issues proactively is key to maintaining momentum.
Maintain a risk register and an issue log to document potential and current problems. Assign owners, establish mitigation plans, and review the status regularly. Conduct risk assessments at set intervals and update the plan as the project evolves.
6. Quality of Deliverables
Quality of deliverables must be assessed to ensure outputs meet the required standards and expectations. Poor quality can lead to rework and client dissatisfaction.
Implement quality assurance and quality control processes, such as peer reviews and testing. Use checklists, acceptance criteria, and client feedback to verify deliverables. Track quality metrics and ensure all issues are addressed before sign-off.
7. Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder engagement should be monitored to confirm that communication is consistent and that expectations are managed. Engaged stakeholders are more likely to support the project and provide timely feedback.
Schedule regular updates, distribute status reports, and hold review meetings. Use collaboration platforms to keep communication transparent and accessible. Monitor feedback and adjust engagement strategies if necessary.
8. Team Performance
Team performance must be evaluated to ensure that team members are meeting productivity goals and contributing to project success. High-performing teams drive better outcomes.
Use performance metrics, feedback loops, and regular check-ins to gauge individual and team output. Provide recognition for achievements and offer support for underperforming areas. Encourage continuous improvement through open dialogue.
9. Communication Effectiveness
Communication effectiveness is crucial for ensuring everyone is informed, aligned, and aware of their responsibilities. Miscommunication can cause delays and confusion.
Monitor communication by tracking message delivery, response times, and meeting participation. Use communication audits and stakeholder surveys to evaluate the clarity and consistency of information shared. Adjust communication plans based on feedback.
10. Compliance and Documentation
Compliance and documentation need to be maintained to meet regulatory standards and provide project transparency. Accurate documentation supports audits and future references.
Track document versions using version control systems. Ensure that all compliance requirements are logged and met according to legal or industry standards. Conduct periodic reviews of documentation to ensure completeness and accuracy.
Monitoring these key components provides a holistic view of project health and improves the ability to respond to challenges proactively. By using the right tools and maintaining consistent oversight, project managers can ensure that their projects are executed successfully and deliver the intended value.
The Role of Communication in Monitoring and Control
The role of communication in monitoring and control is to keep all stakeholders aligned, informed, and engaged throughout the project lifecycle. Clear, consistent communication enables project teams to identify risks early, adjust plans as needed, and maintain transparency across all execution and performance activities.
Effective communication is critical for stakeholder updates. Project sponsors, team members, clients, and third-party vendors rely on timely updates to understand progress, identify issues, and make informed decisions.
Whether through formal reports, email summaries, or collaborative dashboards, updates serve as the primary feedback mechanism that allows stakeholders to assess the health of a project. These communications should include measurable outcomes, task status, budget tracking, and potential risks to ensure everyone stays on the same page.
Weekly or biweekly meetings create a routine for reviewing performance metrics, discussing obstacles, and reassigning priorities based on real-time insights. These sessions offer the opportunity for team members to raise concerns, clarify objectives, and seek guidance from leadership. Recurring check-ins are a cornerstone of the monitoring and control phase because they allow quick detection of scope changes or bottlenecks before they escalate.
Communication also plays a vital role in change control. When adjustments are needed, a well-defined communication protocol ensures that decisions are approved, documented, and communicated clearly to all affected parties. This reduces the risk of misaligned expectations and helps preserve project timelines and deliverables.
Incorporating communication tools into the project environment further strengthens monitoring and control. Platforms such as Microsoft Teams, Slack, or Asana allow real-time updates, centralized documentation, and seamless coordination between team members. These tools not only support day-to-day execution but also provide an audit trail that can be referenced during project evaluations.
Techniques for Project Monitoring and Control
Techniques for project monitoring and control provide structured methods to track progress, manage risks, and ensure that projects stay aligned with their goals. These approaches help project managers make informed decisions, detect issues early, and maintain control over scope, time, and budget.
One of the most widely used techniques is Earned Value Management (EVM). EVM integrates project scope, cost, and schedule to assess overall performance. It provides clear indicators such as Cost Performance Index (CPI) and Schedule Performance Index (SPI), which help project managers determine whether the project is under budget, ahead of schedule, or falling behind. EVM turns abstract progress into measurable data, making it easier to track and report on.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential for ongoing monitoring. These metrics may include schedule variance, cost variance, resource utilization, and task completion rates. KPIs offer a consistent way to evaluate success and identify performance gaps in real time. Selecting relevant KPIs at the start of a project ensures that teams focus on what matters most.
Project dashboards and reporting tools enable real-time visibility into progress. These tools consolidate data from various sources to display performance metrics in an easily digestible format. Dashboards can be customized to show updates for stakeholders, team members, or executive sponsors, helping everyone stay informed and aligned.
Milestone tracking is another technique that segments a project into major checkpoints. By focusing on key deliverables and due dates, project teams can verify whether they are on track or need to adjust. Milestones also help maintain momentum by celebrating small wins and keeping teams focused on the next target.
Change control systems are crucial for managing scope changes. These systems require that any proposed changes be documented, reviewed, and approved before implementation. A disciplined approach to change control prevents scope creep and ensures that adjustments align with project objectives and available resources.
Risk management plans are used during monitoring and control to assess the likelihood and impact of risks. Teams create mitigation strategies and contingency plans that can be activated when needed. Regularly reviewing and updating the risk register helps minimize disruptions and maintain stability.
Time tracking software allows teams to measure how much time is being spent on each task. This technique not only helps manage individual workloads but also reveals whether project estimates were accurate. Time data can be used to optimize future project planning and resource allocation.
Status review meetings are a traditional but highly effective way to monitor progress and control workflow. These meetings bring the team together to discuss blockers, accomplishments, and next steps. Weekly check-ins ensure that no task or issue goes unnoticed.
Gantt charts and critical path analysis are visual techniques that help identify task dependencies and schedule risks. Gantt charts show timelines and task overlap, while critical path analysis pinpoints which activities directly impact the project’s duration. These tools help project managers adjust schedules proactively.
Forecasting techniques such as trend analysis and predictive modeling can be used to anticipate future outcomes. By analyzing current performance data, teams can estimate whether they are likely to meet future milestones or fall short. Forecasting supports better decision-making and helps set realistic expectations with stakeholders.
Together, these project monitoring and control techniques provide the structure and insight needed to keep projects running efficiently. When applied consistently, they lead to improved outcomes, fewer surprises, and greater stakeholder confidence.
This visual outlines eight widely used techniques for project monitoring and control, helping teams track progress, manage performance, and respond proactively to deviations.

Best Practices in Project Monitoring, Control, and Evaluation
Best practices in project monitoring, control, and evaluation are essential for ensuring projects are completed successfully, on time, and within budget. Implementing these practices helps project managers maintain oversight, manage risks, and achieve desired outcomes.
1. Establish Clear Objectives and Performance Indicators
Establishing clear objectives and performance indicators provides a foundation for measuring project success. By defining specific, measurable goals and key performance indicators (KPIs), teams can objectively assess progress and performance. This clarity ensures all stakeholders understand project expectations and evaluation criteria.
2. Develop a Comprehensive Project Plan
Developing a comprehensive project plan outlines the project’s scope, timeline, resources, and risk management strategies. A detailed plan serves as a roadmap, guiding the project team through each phase and facilitating monitoring and control. Regularly updating the plan to reflect changes ensures it remains a relevant tool throughout the project lifecycle.
3. Implement Regular Progress Monitoring
Implementing regular progress monitoring involves systematically tracking project activities and comparing actual performance against the plan. Utilizing tools like Gantt charts and dashboards provides visual representations of progress, enabling early detection of deviations. Consistent monitoring allows for timely interventions to address issues and keep the project on track.
4. Conduct Risk Management Throughout the Project
Conducting risk management throughout the project entails identifying potential risks early and developing mitigation strategies. Regular risk assessments and proactive planning help minimize the impact of uncertainties on project objectives. Maintaining a risk register and updating it as new risks emerge ensures preparedness for unforeseen challenges.
5. Foster Effective Communication Among Stakeholders
Fostering effective communication among stakeholders ensures that all parties are informed and engaged. Establishing clear communication channels and protocols facilitates the timely sharing of information, feedback, and updates. Regular meetings and transparent reporting enhance collaboration and support informed decision-making.
6. Utilize Integrated Project Management Tools
Utilizing integrated project management tools streamlines monitoring and control processes. These tools offer centralized platforms for tracking tasks, resources, budgets, and timelines. Features like real-time reporting and automated alerts assist in identifying issues promptly and maintaining project alignment with objectives.
7. Perform Quality Assurance and Control
Performing quality assurance and control ensures that project deliverables meet predefined standards and stakeholder expectations. Implementing quality management processes, including regular inspections and testing, helps identify defects early. Addressing quality issues promptly prevents costly rework and enhances overall project success.
8. Document Lessons Learned for Continuous Improvement
Documenting lessons learned for continuous improvement involves capturing insights and experiences from the project. Conducting post-project evaluations and creating detailed reports provide valuable information for future projects. Sharing these lessons with the organization fosters a culture of learning and enhances project management practices.
9. Ensure Stakeholder Engagement and Satisfaction
Ensuring stakeholder engagement and satisfaction requires actively involving stakeholders throughout the project. Regularly soliciting feedback and addressing concerns helps align the project with stakeholder needs. Demonstrating commitment to stakeholder interests builds trust and contributes to project success.
10. Adapt to Changes with Flexibility
Adapting to changes with flexibility allows project teams to respond effectively to evolving circumstances. Implementing a structured change management process ensures that modifications are evaluated, approved, and documented. Maintaining flexibility while adhering to project objectives enables teams to navigate challenges and seize opportunities.
By integrating these best practices into project monitoring, control, and evaluation, organizations can enhance their project management capabilities and achieve better outcomes. Consistent application of these strategies leads to improved efficiency, reduced risks, and increased stakeholder satisfaction.
Challenges That Complicate Effective Project Monitoring
Challenges that complicate effective project monitoring often stem from gaps in planning, communication, resource management, or data accuracy. These issues can limit a team’s ability to assess progress, identify risks, and maintain alignment with project objectives. Understanding and addressing these challenges is essential for ensuring that project monitoring delivers timely and actionable insights.
The most common challenges in project monitoring are:
Lack of Clear Performance Metrics
Lack of clear performance metrics makes it difficult to evaluate whether the project is on track. Without predefined key performance indicators (KPIs), teams cannot effectively compare actual performance to the project baseline. This results in vague assessments that delay corrective action.
Teams must define measurable goals for cost, time, quality, and scope to ensure consistency in tracking progress. Metrics should be tailored to the project’s size and complexity and regularly updated to remain relevant throughout the lifecycle.
Poor Communication and Reporting
Poor communication and reporting interfere with the transparency and coordination necessary for monitoring success. When stakeholders and team members are not aligned, critical updates may be missed, and decisions can be delayed.
Establishing a communication plan with regular updates, status reports, and stakeholder engagement ensures everyone is informed. Using collaboration platforms and project dashboards can help consolidate communication and reduce confusion across teams.
Infrequent Monitoring Practices
Infrequent monitoring practices prevent teams from identifying and resolving issues in a timely manner. Waiting too long between performance reviews increases the likelihood of unnoticed risks, missed deadlines, or scope creep.
To address this, project managers should implement continuous monitoring practices. Regular check-ins, milestone reviews, and real-time dashboards help teams respond quickly to changes and keep projects aligned with goals.
Inadequate Use of Technology
Inadequate use of technology hinders visibility and limits the effectiveness of data collection and analysis. Without reliable project management software, teams may rely on manual methods that are error-prone and time-consuming.
Adopting modern tools such as Gantt charts, resource trackers, and cloud-based dashboards improves monitoring accuracy and simplifies decision-making. These tools also provide a central source of truth and reduce the chance of miscommunication.
Resistance to Feedback and Change
Resistance to feedback and change can undermine project monitoring by preventing teams from acting on insights. When stakeholders or team members are reluctant to acknowledge problems or adjust plans, monitoring becomes a formality rather than a decision-making tool.
Encouraging a culture of continuous improvement and open feedback helps build trust and promotes adaptive project behavior. Managers should model responsiveness to insights and reward teams for addressing issues proactively.
Limited Access to Real-Time Data
Limited access to real-time data delays decisions and increases risk during execution. Monitoring based on outdated information can lead to inaccurate conclusions and slow reactions to emerging problems.
To improve responsiveness, teams should integrate monitoring systems that update automatically and reflect the most recent project data. This enables real-time visibility into performance and supports timely corrective action when needed.
Unclear Roles and Responsibilities
Unclear roles and responsibilities disrupt monitoring processes by creating confusion about who owns what. Without designated owners for performance tracking and reporting, issues may go unaddressed or duplicate efforts may occur.
A clear assignment of roles ensures accountability and streamlines monitoring activities. Using a responsibility assignment matrix (such as a RACI chart) can help clarify ownership across all aspects of project monitoring.
Overlooking External Factors
Overlooking external factors reduces the effectiveness of project monitoring by ignoring risks that are outside the immediate project environment. Market changes, supplier delays, or regulatory updates can significantly affect progress and performance.
Successful project monitoring includes horizon scanning and environmental assessment. Building contingency plans and involving external stakeholders early can reduce the impact of these external disruptions.
Most Used Tools for Project Monitoring and Control
Tools for project monitoring and control are usually task-level software platforms that help project managers track progress, assess performance, and maintain alignment with objectives. These tools streamline the process of collecting data, visualizing workflows, and making real-time decisions to keep projects on track.
One of the most widely adopted tools is Microsoft Project. Microsoft Project helps teams develop schedules, assign resources, track progress, and analyze workloads using features such as Gantt charts and timelines. It provides a comprehensive view of project status and allows managers to adjust plans based on performance data.
Jira is another popular tool, especially among Agile and software development teams. Jira supports sprint planning, issue tracking, and real-time collaboration. With customizable dashboards and integration options, Jira enables accurate progress tracking and facilitates daily task management.
Smartsheet combines the familiarity of spreadsheets with powerful project management features. It allows teams to track tasks, set dependencies, and generate reports. Smartsheet’s automation tools also help reduce manual work by triggering updates and reminders based on task status.
Trello offers a user-friendly, visual approach to project monitoring. Trello uses Kanban-style boards, where teams can move tasks across columns to show progress. While it is more lightweight than other tools, Trello is useful for smaller projects or teams that need a simple way to track activity.
Asana is a task-based project management platform that allows teams to organize, assign, and prioritize work. It offers real-time collaboration and status updates, making it easier to keep everyone informed. Asana also provides visual reporting tools to measure task completion and project milestones.
PPM Express is a comprehensive platform designed specifically for project portfolio management and monitoring. It integrates with tools like Microsoft Project, Jira, and Azure DevOps to collect and centralize project data. PPM Express enables managers to visualize portfolio health, monitor KPIs, and evaluate project risks across multiple initiatives.
Other widely used tools include Wrike, ClickUp, and Monday.com, each offering unique features for task tracking, resource management, and performance analysis. These tools support transparency, improve accountability, and help project teams make informed decisions based on accurate data.
While these tools are highly effective for tracking tasks and managing day-to-day execution, large-scale projects often require a more comprehensive solution—one that offers predictive insights across cost, schedule, and risk.
How SEER uses Project Monitoring for better Planning?
SEER® by Galorath is the industry’s leading AI-powered estimation platform, built on over 45 years of expertise and trusted by global innovators including NASA, Lockheed Martin, Boeing, and Accenture. SEER plays a critical role during the project monitoring phase by utilizing the collected data and continuously improving the accuracy of cost, schedule, and risk models which will be used to predict future outcomes.
As real-world data is captured during execution—such as labor hours, costs, and delivery timelines—SEER uses this information to recalibrate forecasts, validate assumptions, and generate more precise estimations for current and future project cycles. This continuous recalibration ensures that project teams maintain alignment between execution and their original objectives.
Using SEER’s parametric models, project managers can compare actual performance against baseline estimates to identify where deviations have occurred and why. These insights not only support mid-project adjustments but also help teams refine future forecasts—building organizational knowledge and improving long-term estimation accuracy.
SEER’s AI capabilities further accelerate this process by enabling intelligent recalculations, contextual learning, and dynamic forecasting based on evolving inputs. Teams can perform what-if analysis and scenario modeling to test the impact of scope changes, resource shifts, or timeline adjustments—selecting the most cost-effective and realistic strategy forward.
By transforming raw project data into insight, SEER helps project leaders stay ahead of risk, prevent overruns, and make evidence-based decisions at every stage. It closes the loop between planning and execution—providing a single source of truth for monitoring performance, strengthening delivery, and learning from every project cycle.