Mastering Cost Risk with the CRED Model: A New Approach to Managing Uncertainty
Project initiation sets the foundation for a successful project by defining its objectives, evaluating feasibility, and aligning stakeholders before planning begins. It represents the first phase of the project lifecycle, where teams determine when to begin, who initiates the work, and why initiation is essential for long-term success. Knowing when to initiate a project depends on satisfying basic preconditions such as identifying a clear need, gaining early buy-in, and securing exploration resources. Projects are typically initiated by sponsors and managers who define high-level objectives and align them with organizational priorities.
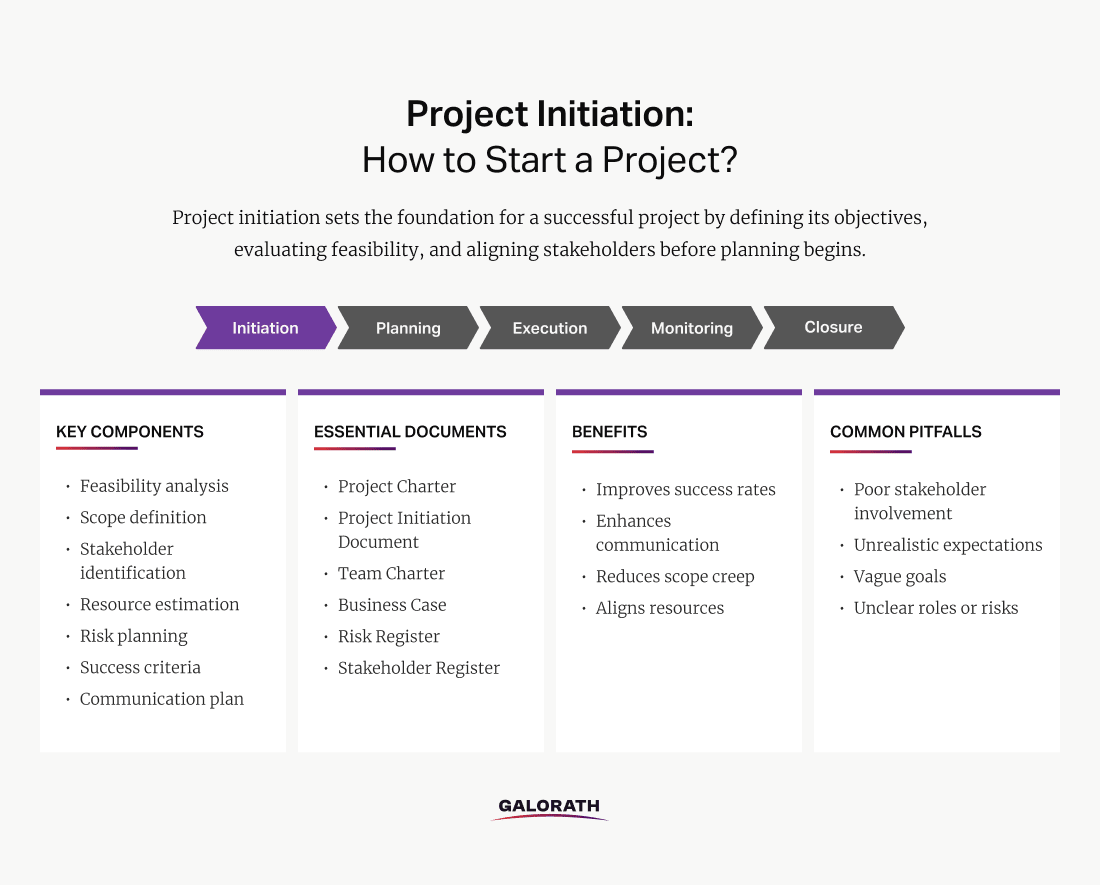
Understanding the importance of project initiation helps reduce risks, increase buy-in, and guide downstream decision-making with clarity. Strong initiation practices create a unified vision, identify early risks, and foster stakeholder alignment. These benefits are reinforced by focusing on ten key components of initiation, including feasibility analysis, scope definition, stakeholder identification, resource estimation, risk planning, success criteria, and a communication plan. These elements provide the structural backbone of a strong project launch.
Effective initiation relies on producing several key documents that formalize scope, expectations, and team structure. These include the Project Charter, Project Initiation Document (PID), Team Charter, Business Case, Risk Register, and Stakeholder Register. Together, these documents provide the foundation needed to drive execution and manage stakeholder expectations throughout the project lifecycle.
When executed well, project initiation improves success rates, enhances communication, reduces scope creep, and ensures that resources are allocated realistically. Benefits include clearer goal alignment, proactive risk mitigation, and improved resource utilization. Strong initiation enables projects to meet deadlines, stay on budget, and deliver the intended value.
However, teams must also be aware of common difficulties during initiation that can lead to project failure. These include poor stakeholder involvement, vague goals, unrealistic expectations, and unclear roles or risks. Overlooking any of these factors may result in misalignment, resistance, or delays later in the project lifecycle.
A project kickoff meeting is an essential part of project initiation that introduces the team, clarifies expectations, and reviews objectives and roles. A strong kickoff agenda includes introductions, a project overview, communication guidelines, and a Q&A session to address concerns before formal planning begins.
The following visual outlines the core components of the project initiation phase, including key elements, essential documents, expected benefits, and common pitfalls teams should be aware of.
What is project initiation?
Project initiation, often referred to as the initiation stage of a new project, is the earliest phase in the project lifecycle, where teams and stakeholders define the high-level scope, objectives, and feasibility of what they aim to accomplish.
It’s also commonly called the project initiation phase, project inception, or even the project management initiation phase, reflecting its pivotal role in outlining how to start a project and how to begin a project. The initiation process is when you formulate your initial plan, ensuring you have a clear project intro before committing significant resources.
One experienced project manager put it this way: “Without proper initiation, you’re simply hoping for success rather than planning for it.” This statement underscores the vital importance of initiating a project with diligence and foresight. By thoroughly starting a new project at this stage, you identify core objectives, define success criteria, and lay out the potential constraints or risks. All these efforts lead to a more confident project launch and higher chances of achieving the intended outcomes.
The initiation phase of a project also provides the structure for subsequent activities, such as establishing a project vision, securing stakeholder buy-in, and verifying the project’s overall feasibility. It ensures that everyone on the team knows why the work is necessary and what the end goal looks like, long before any detailed planning or execution begins.
By taking the time to perform a thoughtful project initiation, organizations are better equipped to allocate resources wisely, address uncertainties early, and maintain clear communication from day one.
When Is the Best Time to Begin the Project Initiation Phase?
Deciding when to start with the project initiation is crucial for project success. If you dive in too early and don’t have enough information, you may waste resources on a project that lacks clear direction. On the other hand, waiting too long to initiate a project can lead to missed opportunities or stakeholder disengagement. Striking the right balance helps to begin a project effectively, ensuring that you have sufficient data to define your project’s viability but not so much that you lose momentum.
Preconditions for Project Initiation
Before fully committing to the initiation stage of a new project, most experts suggest meeting a few essential conditions:
- A Clearly Identified Problem or Opportunity
You should have a well-defined need or opportunity driving the project. Whether it’s addressing a gap in the market or solving an internal workflow challenge, this clarity ensures you know why you’re starting a new project in the first place. - Preliminary Stakeholder Buy-In
Gathering initial support from decision-makers and influencers is critical. Without this buy-in, you risk misalignment later on, which can derail your project launch before it gains momentum. Early consensus helps validate the project intro and secures a base level of commitment. - Resources or Budget Allocated for Exploration
While you don’t need a fully fleshed-out plan yet, having at least some resources earmarked for discovery is important. This might include seed funding, access to key personnel, or time set aside for a feasibility study—anything that allows you to develop an initial plan without jeopardizing other priorities.
As soon as you’ve satisfied the basic preconditions, you have enough to outline a strong initial plan, provide a clear project intro for the broader team, and ensure everyone understands the mission and feasibility. By doing so, you reduce the risk of costly course corrections later and give the project every chance of success.
The best time to begin project initiation is as soon as you have a validated need, initial stakeholder support, and basic resources to explore the problem in detail.
Who Initiates the Project?
Projects usually begin when senior stakeholders recognize a business need or a clear business opportunity. These stakeholders may include executives, department heads, or external clients. They see the potential benefit of the project and decide that it is worth pursuing. At this early stage, people with the authority to allocate funds or resources often step in.
The project sponsor often holds the highest level of accountability. The sponsor’s role is to provide support, secure funding, and align the project with broader organizational goals. The sponsor makes sure that the project’s direction follows the company’s vision and mission. When questions about priority or scope arise, the sponsor helps resolve them.
The project manager also plays an important part, especially during the initiation phase. The project manager prepares early documentation. They gather initial requirements, engage with stakeholders, and start outlining the plan. Although the project manager drives much of the day-to-day work, the overall accountability rests with the project sponsor. This balance of roles helps keep the project on track.
Why is project initiation important?
The main objective of an initiation project phase is to ensure that everyone understands the project’s purpose, feasibility, and success criteria before larger investments of time and resources are made.
One important reason to focus on project initiation is that it establishes a unified vision. A clear vision aligns stakeholders. It clarifies the overall project intro. When everyone understands the project goals, conflicts become less likely. The team can work more efficiently.
Another reason is that early risk identification is essential. By starting early, potential risks or constraints can be spotted quickly. This helps the team plan risk mitigation strategies. It keeps the project on track before more resources are committed.
A third reason is the need to secure stakeholder buy-in. Early support from key decision makers is critical. Stakeholders provide essential resources and guidance. Their commitment builds trust. It ensures that the project receives the necessary funding and backing.
Project initiation creates a clear roadmap, and a good initial plan informs the detailed planning stage that comes next. When the project is well initiated, each following phase runs more smoothly.
What are the 10 key components of Project Initiation?
The key components of project initiation serve a clear purpose, to ensure the initiation phase sets up your project for success. Here are the 10 essential Project Initiation components:
1. Feasibility Assessment
A feasibility assessment evaluates if your project can realistically succeed. Project feasibility examines technical requirements. It also reviews available resources and funding. The goal is to prevent investing in unachievable projects.
2. Scope Definition
Scope definition outlines exactly what the project will deliver. It sets clear boundaries. It defines what is included and excluded. Clear scope prevents misunderstandings and scope creep.
3. Stakeholder Identification
Stakeholder identification determines who is impacted by your project. It includes executives, users, or external clients. This step ensures key individuals support the project. It also clarifies communication channels.
4. Risk Identification
Risk identification highlights potential obstacles early on. It considers factors like technology challenges and resource constraints. Addressing risks upfront minimizes surprises later.
5. Resource Estimation
Resource estimation determines the initial needs for staff, materials, and funding. Accurate estimation helps secure budgets. It supports realistic timelines and manageable workloads.
6. Project Charter Development
Creates a formal document that authorizes the project and outlines its objectives, scope, stakeholders, risks, constraints, and assigned leadership. The charter serves as a high-level agreement that aligns teams and sponsors before execution begins.
7. Goal Definition
Clearly defined goals keep stakeholders aligned. Goals should be specific and measurable. Clear goals help teams stay motivated and focused throughout the project.
8. Initial Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Breaks the project into smaller, manageable components. An initial WBS offers early visibility into major deliverables and helps teams begin resource planning and scheduling.
9. Initial Communication Plan
An initial communication plan outlines how information will be shared. It defines communication methods and frequency. Clear communication keeps everyone aligned and informed.
10. Success Criteria
Defining success criteria makes expectations explicit. It includes measurable outcomes and milestones. Clarity around success criteria guides decisions during the project.
Project Initiation Vs Project Planning
Project planning, following the project initiation phase, is where the initial vision is transformed into a detailed and actionable roadmap. While initiation sets the strategic foundation by defining the project’s purpose, objectives, and feasibility, planning focuses on breaking down that foundation into specific tasks, timelines, resource allocations, and measurable milestones.
During the planning phase, project managers and teams collaborate to create comprehensive schedules, assign roles and responsibilities, estimate costs, and clearly define deliverables. Planning ensures that every aspect of the project is well-structured and understood, providing a practical framework for successful execution and ongoing progress evaluation.
6 Types of Project Initiation Documentation
The project initiation phase involves more than just defining objectives — it is about creating a complete set of documents that will serve as the backbone of the project moving forward. These documents provide structure, support decision-making, and ensure everyone involved shares a common understanding of the project.
They help set the project’s direction, define roles and responsibilities and without this essential documentation, projects risk misalignment, confusion, and uncontrolled changes as they progress.
Among the most common project initiation documents are charters, registers, and cases each serving a specific purpose. They collectively formalize the project’s existence, clarify why it is being undertaken, identify who is involved, and establish how the team will work together.
Project Charter
The first document in a project is the Project Charter, which formally authorizes the project and defines high-level goals and objectives. It identifies key stakeholders and establishes the authority of the project manager. Additionally, it outlines the main scope, budget estimates, and general timelines. Stakeholders refer to the charter for initial guidance throughout the project lifecycle.
Project Charter vs Project Plan
The project charter is created first. It provides high-level information such as objectives, scope, and approval. A project plan, however, is more detailed and created later. It outlines specific tasks, timelines, budgets, and resources. The charter authorizes the project, while the plan guides its execution.
Project Initiation Document (PID)
The Project Initiation Document (PID) provides detailed information necessary for stakeholders to understand the project clearly. It includes clearly defined scope, detailed goals, key milestones, and project boundaries. A PID also outlines roles and responsibilities, timelines, success criteria, and how the project aligns with organizational strategy. It becomes a reference for stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle.
Team Charter
The team charter focuses specifically on the project team itself. It establishes clear norms and expectations for team interactions. This document includes communication guidelines, responsibilities, expectations, and conflict-resolution strategies. Having a team charter ensures everyone agrees on how to collaborate effectively from the very beginning.
Business Case
A business case justifies why the project is necessary and beneficial. It provides detailed reasoning for initiating the project. This document typically includes the problem or opportunity the project addresses. It also demonstrates how the project adds value to the organization. The business case helps stakeholders understand the financial and strategic benefits before approving the project.
Stakeholder Register
The stakeholder register lists all individuals, groups, or organizations with interest or influence on the project. It identifies their roles, expectations, level of influence, and communication preferences. Maintaining a stakeholder register ensures important voices are considered from the very start of the initiation process.
Risk Register
The risk register identifies potential risks early in the initiation stage. It documents potential risks, their probability, impact, and initial strategies to address them. Identifying risks early allows teams to prepare solutions proactively, reducing negative impacts during project execution.
The visual below presents six essential documents used during the project initiation phase, each playing a critical role in setting the stage for successful planning phase.

Benefits of a Well-Executed Project Initiation
A well-executed initiation ensures all stakeholders clearly understand the project’s purpose, feasibility, and expected outcomes. This clarity helps establish consensus among stakeholders early, aligning their expectations.
Stakeholders appreciate transparency about project scope, timelines, and goals. When stakeholders feel involved early, they’re more likely to offer active support. Early involvement also reduces resistance later in the project lifecycle.
A comprehensive project initiation phase also reduces uncertainty. Early risk identification allows mitigation strategies to be set proactively. It prevents surprises that could delay or derail project progress. As uncertainty decreases, confidence in project execution grows.
Effective initiation reduces the risk of scope creep. Clear initial documentation and well-defined success criteria make it easier to maintain project focus. It prevents unnecessary expansions or misalignments that drain resources and budget. Properly initiated projects remain streamlined and aligned with their original objectives.
In addition, thorough initiation boosts resource management. Clear early planning ensures resources—financial, human, and material—are allocated accurately. Better initial resource allocation reduces waste, avoids conflicts, and sets realistic expectations.
Finally, strong project initiation contributes directly to overall project outcomes. Projects that start clearly are more likely to meet their goals, stay within budget, and finish on time, with the higher overall success rates.
Common Obstacles and Difficulties During Project Initiation
Challenges often arise during the project initiation phase. It’s common for teams to encounter difficulties even before formal planning begins. Recognizing and addressing these obstacles in the project initiation phase can save significant resources and reduce risks later.
Inadequate Stakeholder Involvement
One common difficulty during the initiation stage is insufficient stakeholder involvement. Sometimes key stakeholders are not identified clearly at the start. Without early stakeholder input, teams risk overlooking critical information. Stakeholders may also feel disconnected from the project’s goals. This disconnection can cause confusion or resistance in later stages.
It’s important to consider that stakeholders who aren’t engaged early may challenge key decisions later. This challenge can disrupt timelines and cause delays. Engaging stakeholders early in the initiation process helps prevent these issues.
Unclear Objectives
Another frequent issue during project initiation is unclear or poorly defined objectives. Projects with vague goals are difficult to manage. They lead to confusion and can result in misalignment among stakeholders and create disagreements within teams. Teams may interpret project goals differently, leading to conflicting efforts. Clarifying objectives early helps reduce ambiguity and measure project success transparently.
Insufficient Resources or Budget
Projects often start with unclear or unrealistic expectations about resources. This includes budgets, staff, equipment, or tools needed. Underestimating required resources during initiation can lead to shortages later. These shortages create significant roadblocks once the project is underway.
Poor Risk Identification
Failing to identify risks early can severely impact a project. Teams sometimes overlook potential risks in their eagerness to start quickly. This oversight can leave projects unprepared to handle obstacles.
Lack of Clearly Defined Roles and Responsibilities
When team members don’t clearly understand their duties, it results in confusion, which slows decision-making and lowers productivity. Clarifying roles and responsibilities early helps teams collaborate smoothly. It ensures everyone knows what they’re accountable for from the start.
Unrealistic Expectations or Over-Ambition
Project teams sometimes set overly ambitious goals during initiation. High enthusiasm at the start may lead to unrealistic expectations. When reality sets in, projects can become overwhelmed. Teams should balance ambition with achievable milestones. This balanced approach reduces frustration and promotes realistic planning.
Can Projects Go Wrong in the Initiation Phase?
Yes, projects can certainly go wrong during the initiation phase. The initiation phase is critical for project success, yet mistakes occur frequently at this stage. Problems arise if teams rush through initiation or neglect important details. Such oversights set the stage for challenges later in the project lifecycle.
One common cause of failure during project initiation is rushing through essential steps. Teams may feel pressured to begin quickly. When this happens, they overlook defining clear objectives. They might also skip important stakeholder consultations. As a result, key participants become misaligned on project goals.
Misalignment of stakeholder expectations delays progress and jeopardizes the project’s success. Stakeholders may have different understandings of the project’s purpose or scope. This confusion leads to conflicts later on. Resolving these conflicts can consume extra time and resources and even lead to project abortion or failure.
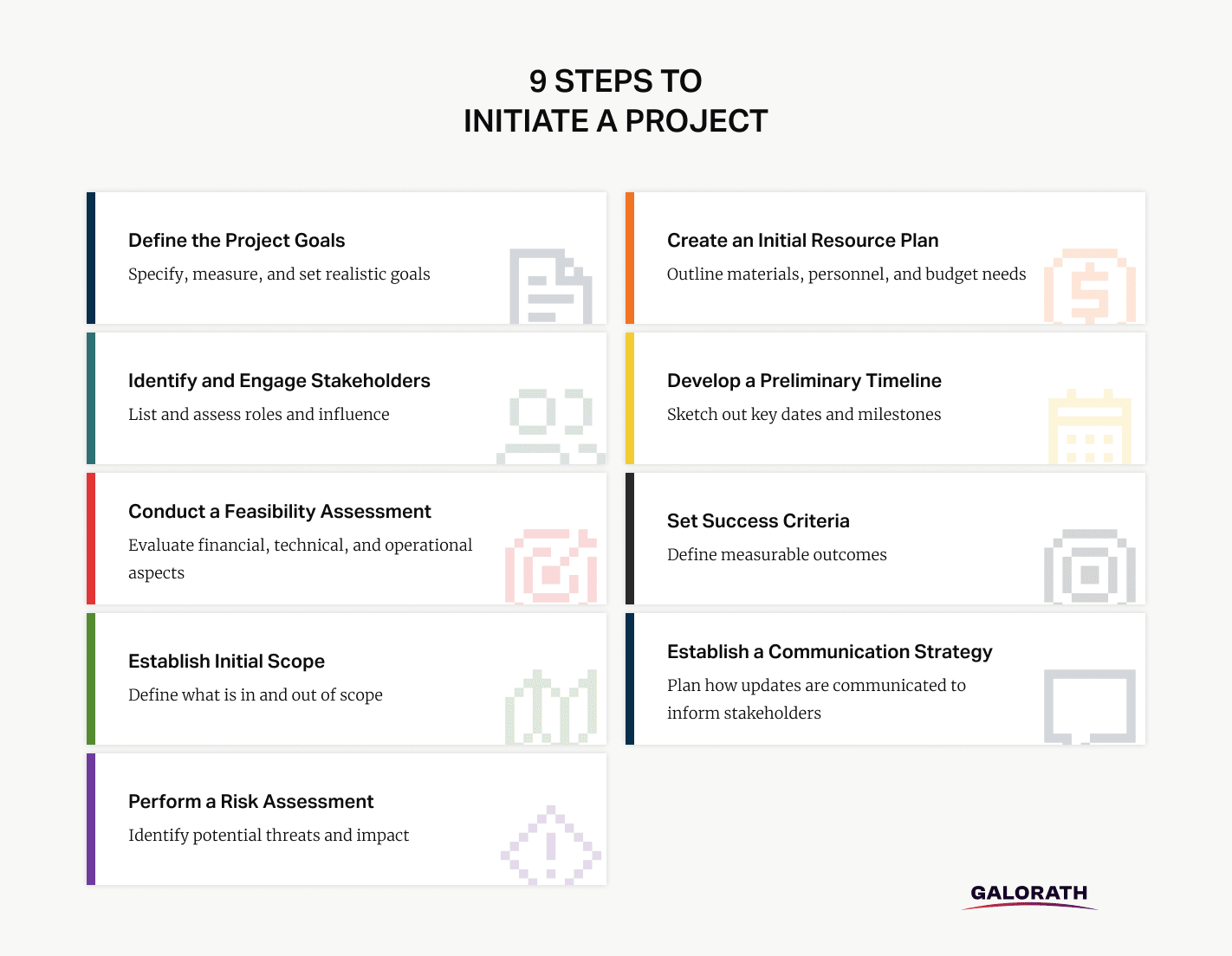
9 Steps to Initiate a Project
Starting a new project requires a clear, structured approach. Initiating a project is the first crucial phase in the project management lifecycle. Proper initiation sets a solid foundation, reduces confusion, and ensures alignment among stakeholders. Below are key steps for effectively initiating any new project.
1. Define the Project Goals
Clearly define your project goals. Goals should describe exactly what the project aims to achieve. Goals must be specific, measurable, and realistic. Clarify why the project matters to your organization. Defining clear objectives helps align everyone involved. It provides a reference point throughout the project’s lifecycle.
2. Identify and Engage Stakeholders
Stakeholder identification is a critical step. First, list individuals or groups affected by the project. Then assess their roles, interests, and influence levels. Early engagement ensures everyone understands the project’s purpose. It also builds commitment and early support. Keep stakeholders informed throughout the initiation process. Early engagement reduces confusion and fosters collaboration.
3. Conduct a Feasibility Assessment
Feasibility assessment evaluates if the project can realistically succeed. Consider financial, technical, operational, and resource constraints. Conducting a feasibility analysis helps prevent investing resources into unrealistic initiatives. Early identification of obstacles ensures they can be addressed proactively.
4. Establish Initial Scope
Clearly defining the project’s initial scope is essential. Scope definition outlines exactly what the project includes and excludes. Clarifying the scope sets boundaries and prevents misunderstandings. It also reduces the risk of scope creep. Teams can refer back to the defined scope when making decisions later.
5. Perform a Risk Assessment
Risk assessment identifies potential issues before they become problems. List potential threats and their possible impact on project outcomes. Risks can include budget overruns, delays, resource shortages, or technical difficulties. Understanding risks early allows for effective mitigation strategies.
6. Create an Initial Resource Plan
An initial resource plan outlines what materials, personnel, and budget the project requires. Determine preliminary estimates for staffing needs, equipment, and tools. An early resource estimate helps secure the necessary funding and personnel. It ensures that projects do not start without adequate support.
7. Develop a Preliminary Timeline
Draft an initial timeline to identify key milestones and project phases. Sketching out key dates and milestones provides structure and sets expectations. This timeline ensures stakeholders understand important checkpoints. It also helps teams visualize the sequence and duration of activities.
8. Set Success Criteria
Establishing clear success criteria early helps measure progress. Define measurable outcomes to evaluate the project’s effectiveness. Clear success criteria support transparent communication about project achievements. They provide benchmarks for ongoing monitoring and final evaluation.
9. Establish a Communication Strategy
A preliminary communication plan clarifies how project updates are shared. Outline communication methods, frequency, and stakeholder reporting responsibilities. Clear communication ensures stakeholders remain informed throughout the project. Effective communication minimizes misunderstandings and keeps everyone aligned.
By following these structured steps, project initiation becomes systematic and organized. It reduces uncertainty, aligns stakeholders, and sets a firm foundation for future phases. Initiating projects in a structured manner increases the likelihood of success and ensures smoother project execution.
The following visual outlines nine clear steps to initiate a project effectively, providing a structured approach to move from idea to actionable plan.
What is a Project Kickoff Meeting?
A project kickoff meeting is an official event to formally introduce a new project to all stakeholders involved. It is sometimes called a kick off call, kick off conference, or project kickoff presentation. The main goal of this meeting is to review the project inception meeting agenda with stakeholders. A successful kickoff helps teams clarify roles, confirm deliverables, and establish communication guidelines.
During the kickoff meeting, participants gain clarity about project objectives. The meeting ensures that all stakeholders understand their roles from the start. It also sets expectations for future communications and interactions.
This image provides an overview of the project kickoff—what it is, why it matters, and the key components typically covered during a successful kickoff meeting, including goals, roles, timelines, and communication protocols.
The visual below highlights what a kickoff meeting entails, including his relevant parts.

Relevant Parts of a Project Kickoff Meeting
A successful project kickoff meeting sets the tone for the entire project. Below are the key components of a project kickoff that should be included to ensure alignment, clarity, and momentum from day one.
Agenda
A clear agenda is essential for a productive project kickoff meeting. It outlines the main objectives of the meeting. The agenda should list key discussion topics, project timelines, and major milestones. Clearly defined roles and responsibilities should also appear in the agenda. Having a structured agenda keeps the meeting organized and focused.
Introductions
Introductions are important at kickoff meetings. Each participant introduces themselves and their role within the project. Stakeholders explain their area of expertise and responsibilities. Clearly understanding who does what builds trust among team members. It also helps streamline future communications.
Project Overview Presentation
A project kickoff usually includes a detailed presentation. The presentation covers the project’s background, scope, and objectives. It often highlights key goals, expected outcomes, and success criteria. The presentation ensures everyone has the same understanding of the project.
Communication Guidelines
Defining communication guidelines is crucial at the project kickoff. Stakeholders discuss how often updates will be shared. They determine communication channels like emails, calls, meetings, or shared digital platforms. Clear guidelines prevent miscommunications later in the project.
Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly stating roles and responsibilities prevents confusion. During the kickoff meeting, each participant learns their specific role. Project managers confirm who makes key decisions. Clarifying roles reduces future conflicts and keeps the project on track.
Open Q&A
An open question-and-answer session is included at the end of the kickoff meeting. Stakeholders voice any concerns, doubts, or suggestions. Addressing these questions early reduces misunderstandings. It allows issues to be resolved before they become significant obstacles.
What is the Next Step Taken After Project Initiation?
The next step after project initiation is the project planning phase. After initiation, stakeholders approve moving forward. Planning involves developing detailed schedules, tasks, and resource allocation. During this phase, project managers and teams create precise timelines and clearly define tasks.
Project planning translates initiation goals into actionable steps. It includes assigning resources and defining roles clearly. Teams establish detailed project milestones, identify risks, and develop strategies to manage them. Planning creates the necessary framework for successful project execution. Clear initiation ensures the planning phase proceeds efficiently.